The On-Line Calculation fields are as i)Agriculture ii) Aircraft iii)General Math iv)Physics v)Chemistry vi)Chemical Engg. vii)Civil Engg. viii)Mechanical Engg. ix)EEC Engg. x) Fisheries Engg. xi) Poultry Engg. xii) Merine Engg. xiii) Nuclear Engg. xiv) Accounting and Finance. and many more. They assist Students, engineers, and researchers in analyzing and optimizing their regular work. It is the Blogpost for continuous use and I am requesting you to share as much as you can.
Donate for the Poorest Students
You can support for the poorest students. Copy the link in your browser & Donate as small as possible..
https://www.paypal.com/donate/?hosted_button_id=R3MNE48JU7KGL
Tuesday, 11 July 2023
Heat Exchanger Network Design Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Evaporation Calculator Designs and analyzes evaporation processes for liquid concentration :Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Evaporation Calculator
Drying Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Drying Calculator
Crystallization Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Crystallization Calculator
Gas-Liquid Absorption Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
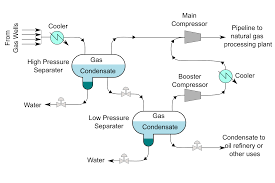
Definition: Gas-liquid absorption is a mass transfer operation where a soluble gas is transferred from a gas phase to a liquid phase.
Click the Translate button(see right) on this post to set your Own Language to understand more perfectly!!
Gas-Liquid Absorption Calculator
Definition Continue: Gas-Liquid Absorption
Gas-liquid absorption is a mass transfer operation where a soluble gas is transferred from a gas phase to a liquid phase. Key parameters influencing this process include:
Key Factors:
Gas Flow Rate (m³/hr): The volume of gas passing through the absorber per hour.
Liquid Flow Rate (m³/hr): The volume of liquid used to absorb the gas per hour.
Gas Concentration (%): The concentration of the target gas in the inlet gas stream.
Liquid Concentration (%): The concentration of the absorbed gas in the liquid phase at the outlet.
Sample Values:
Gas Flow Rate: 1000 m³/hr
Liquid Flow Rate: 500 m³/hr
Gas Concentration: 5% (v/v)
Liquid Concentration: 2% (w/w)
Calculation Example:
Calculating Gas and Liquid Mass Flow Rates:
Assuming air as the carrier gas with a density of 1.2 kg/m³:
Gas mass flow rate = Gas flow rate * Gas density = 1000 m³/hr * 1.2 kg/m³ = 1200 kg/hr
Assuming water as the absorbing liquid with a density of 1000 kg/m³:
Liquid mass flow rate = Liquid flow rate * Liquid density = 500 m³/hr * 1000 kg/m³ = 500000 kg/hr
Calculating Mass Transfer Rate:
This requires additional information about the system, such as equilibrium relationships, mass transfer coefficients, and column dimensions.
Additional Considerations:
Equilibrium Relationship: Describes the distribution of the gas between the gas and liquid phases at equilibrium.
Mass Transfer Coefficients: Quantify the rate of mass transfer across the gas-liquid interface.
Column Design: The type of absorber (packed bed, plate column) and its dimensions affect mass transfer efficiency.
Operating Conditions: Temperature, pressure, and liquid properties influence the absorption process.
Example Calculation (Simplified):
Assuming a simple system with a linear equilibrium relationship and constant mass transfer coefficients, we can estimate the outlet gas concentration.
Overall mass transfer coefficient: K = 0.1 (made-up value for illustration)
Contact time: 2 minutes
Mass transfer rate: N = K * A * (Cgi - Cgi*)
Where N is the mass transfer rate, A is the contact area, Cgi is the inlet gas concentration, and Cgi* is the gas concentration at the interface.
Outlet gas concentration: Cge = Cgi - (N / (G * Cp))
Where Cge is the outlet gas concentration, G is the gas mass flow rate, and Cp is the gas specific heat capacity.
Note: This is a highly simplified example. Actual calculations involve complex mass transfer models and experimental data.
Gas-liquid absorption is a complex process influenced by various factors. A thorough understanding of these factors is essential for designing efficient absorption systems.
Let's Delve Deeper into Gas-Liquid Absorption
Specific Applications of Gas-Liquid Absorption
Gas-liquid absorption finds applications in various industries. Let's explore a few:
Industrial Processes:
Removal of acid gases (CO2, H2S) from industrial flue gases.
Recovery of valuable components (e.g., ammonia, organic solvents) from process streams.
Air pollution control (scrubbing of NOx, SOx).
Environmental Protection:
Removal of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from industrial emissions.
Treatment of wastewater containing dissolved gases.
Chemical Industry:
Production of various chemicals through absorption processes (e.g., sulfuric acid, nitric acid).
Deeper Dive into Calculation Methods
Gas-liquid absorption calculations can be complex, involving mass transfer principles, equilibrium relationships, and column design. Let's explore some key aspects:
Mass Transfer Coefficients: These quantify the rate of mass transfer across the gas-liquid interface. Correlations and experimental data are often used to estimate these coefficients.
Equilibrium Relationships: Describe the distribution of the gas between the gas and liquid phases at equilibrium. Henry's law is commonly used for dilute solutions.
Column Design: Factors like column height, diameter, packing type, and liquid distribution affect the overall performance of the absorber. Numerical Methods: For complex systems, numerical methods (e.g., finite difference, finite element) can be employed to solve mass transfer equations.
How is it possible to Earn Money using the knowledge of Gas-Liquid Absorption Calculation in our practical life?????
Monetizing Gas-Liquid Absorption Knowledge
Understanding gas-liquid absorption is crucial in various industries. Here's how this knowledge can be monetized:
Consulting Services
Process Optimization: Help industries improve the efficiency of their gas-liquid absorption processes by analyzing performance data, identifying bottlenecks, and recommending improvements.
Equipment Design: Provide expertise in designing and sizing absorption equipment (columns, packings, etc.) to meet specific process requirements.
Troubleshooting: Assist in diagnosing and resolving issues in existing absorption systems.
Research and Development
New Absorbent Development: Research and develop novel absorbents with enhanced mass transfer properties for specific applications.
Process Improvement: Investigate and implement new technologies to improve absorption efficiency and reduce operating costs.
Sales and Marketing
Equipment Sales: Sell absorption equipment and related components to industries requiring gas-liquid separation.
Chemical Sales: Sell solvents or other chemicals used in absorption processes.
Education and Training
Workshops and Seminars: Conduct training programs on gas-liquid absorption principles and design for engineers and operators.
Online Courses: Develop online courses on the subject.
Other Avenues
Expert Witness: Provide expert testimony in legal cases involving gas-liquid absorption processes.
Technical Writing: Write articles, papers, or books on gas-liquid absorption technology.
Key to success:
Deep understanding of mass transfer principles and absorption equipment.
Strong problem-solving and analytical skills.
Ability to communicate complex technical information to a diverse audience.
Networking with industry professionals to stay updated on the latest advancements.
By effectively applying your knowledge of gas-liquid absorption, you can create value for industries and generate income through various avenues.
Do YOU Want To Earn Money In Various Ways, Click The Link & Explore Your Field of Interest!!!
Thermal Conductivity Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Thermal Conductivity Calculator
Heat Exchanger Fouling Resistance Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Heat Exchanger Fouling Calculator
Mixing Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Mixing Calculator
Process Control Loop Tuning Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Process Control Loop Tuning Calculator
Vapor Pressure Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Vapor Pressure Calculator
Pressure Relief Valve Sizing Calculator:Calculators for Students, Engineers & Researchers:free Online Tool
Pressure Relief Valve Sizing Calculator
Results:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
QR Code Generator:Engineering & Science Calculators: Free Online Tools.
Definition: A *QR code* (Quick Response code) is a two-dimensional barcode that stores data, like text, URLs, or other digital information, ...

-
Definition: An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane where the sum of the distances from each point to two fixed points (called foci) ...
-
Definition: A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning it contains at least one term that is squared. Clic...