Definition: A Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tool is a software application or system designed to assist farmers and agricultural professionals in optimizing irrigation practices for crops. It takes into account various factors such as crop water requirement, soil moisture levels, and weather forecast to determine the timing and amount of irrigation needed.
Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tool
Definition Continue: Here's a breakdown of the components and calculations typically involved:
Crop Water Requirement (CWR):
Crop Evapotranspiration (ETc): The amount of water lost from the soil through evaporation and transpiration by the crop.
Reference Evapotranspiration (ETo): The amount of water lost from a well-irrigated grass surface, calculated based on meteorological data.
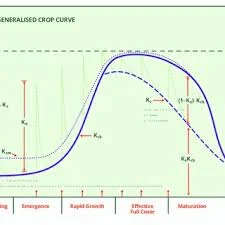
Crop Coefficient (Kc): A factor representing the water requirements of specific crops at different growth stages.
Net Irrigation Requirement (NIR): The difference between ETc and rainfall.Equation:𝐸𝑇𝑐=𝐾𝑐×𝐸𝑇𝑜
Soil Moisture: Soil Moisture Content: Measured or estimated moisture level in the soil. Field Capacity (FC): The maximum amount of water the soil can hold against gravity. Permanent Wilting Point (PWP): The soil moisture content at which plants can no longer extract water effectively.
Weather Forecast: Rainfall: Predicted or observed precipitation. Temperature: Forecasted temperatures influence evapotranspiration rates. Humidity: Affects the rate of evaporation from soil and transpiration from plants. Wind Speed: Influences the rate of evaporation.
Irrigation Scheduling: Soil Moisture Monitoring: Continuous or periodic measurement of soil moisture levels using sensors or probes. Threshold-based Irrigation: Triggering irrigation when soil moisture falls below a certain threshold. Time-based Irrigation: Applying water at specific intervals based on historical data or crop growth stage.
The Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tool integrates these factors and calculations to provide recommendations for when and how much water to apply to the crops. It can generate schedules, alerts, and reports to help farmers make informed decisions, optimize water usage, and maximize crop yield while conserving resources. The tool may also incorporate machine learning algorithms to improve accuracy over time by learning from historical data and feedback.
How farmers benefited from the Crop irrigation scheduling tool calculator
Farmers benefit from Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tools in several ways:
1. **Optimized Water Usage**: By accurately calculating crop water requirements based on factors like evapotranspiration, soil moisture, and weather forecasts, farmers can ensure that they apply just the right amount of water needed by the crops. This prevents both over-irrigation, which can lead to waterlogging and nutrient leaching, and under-irrigation, which can result in yield losses. *Example*: A farmer using an irrigation scheduling tool notices that due to recent rainfall and low temperatures, the soil moisture level is higher than usual. The tool advises reducing irrigation frequency to prevent waterlogging and save water, resulting in cost savings and healthier crops.
2. **Increased Crop Yield**: By providing optimal irrigation schedules tailored to specific crop needs and growth stages, these tools can help maximize crop yield. Ensuring that crops receive sufficient water at critical growth stages promotes healthy plant development and higher productivity. *Example*: A farmer using an irrigation scheduling tool for their vineyard receives recommendations to increase irrigation during the flowering and fruiting stages of the grapevines. By following these recommendations, the farmer achieves larger grape yields and higher-quality fruit for winemaking.
3. **Resource Conservation**: Efficient irrigation scheduling helps conserve water resources by reducing wastage through runoff and evaporation. By using water more judiciously, farmers can contribute to sustainable agriculture and minimize their environmental impact. *Example*: A farmer in a water-stressed region adopts an irrigation scheduling tool that takes into account real-time weather data and soil moisture levels. By implementing precise irrigation practices, the farmer reduces water usage by 20% while maintaining crop yields, thus conserving a scarce resource and contributing to environmental sustainability.
4. **Cost Savings**: By optimizing water usage and improving crop yields, farmers can reduce input costs associated with irrigation, such as water bills, energy for pumping, and labor. Additionally, by preventing water-related issues like waterlogging or salinization, farmers can avoid costly crop losses. *Example*: A farmer using an irrigation scheduling tool notices a decrease in water usage and energy costs after implementing the recommended irrigation schedule. With fewer irrigation cycles and reduced risk of water-related crop damage, the farmer saves money on both water and electricity bills.
In summary, Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tools empower farmers with data-driven insights to make informed decisions about irrigation, leading to improved crop yields, resource conservation, cost savings, and overall sustainable agricultural practices.
How To Earn Money Using Irrigation Scheduling Tool.
There are several potential ways to monetize a Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tool:
1. **Subscription Model**: Offer the tool as a subscription-based service to farmers and agricultural professionals. Subscribers would pay a monthly or annual fee to access the tool's features, including crop water requirement calculations, soil moisture monitoring, weather forecasts, and personalized irrigation schedules.
2. **Tiered Pricing Plans**: Provide different tiers of service based on the needs of users. Basic plans could include essential features, while premium plans could offer advanced analytics, support for a wider range of crops, or integration with other farm management systems.
3. **Consulting Services**: Offer consulting services to farmers who require additional assistance in interpreting the tool's recommendations and implementing irrigation practices effectively. This could include on-site visits, personalized training sessions, or custom irrigation planning services.
4. **Custom Development**: Develop custom versions of the tool tailored to specific crops, regions, or agricultural practices for individual clients or organizations. Charge a one-time fee or ongoing royalties for the development and licensing of these custom solutions.
5. **Data Monetization**: Aggregate and anonymize data collected from users of the tool and sell insights or analytics derived from this data to agricultural companies, research institutions, or government agencies interested in trends related to crop irrigation and water usage.
6. **Partnerships and Integrations**: Partner with agricultural equipment manufacturers, irrigation companies, or other stakeholders in the agricultural industry to integrate the tool with their products or services. Earn revenue through referral fees, licensing agreements, or revenue sharing arrangements.
7. **Training and Workshops**: Offer training programs, workshops, or webinars to educate farmers and agricultural professionals on the principles of irrigation scheduling, the use of the tool, and best practices for water management in agriculture. Charge a fee for participation in these training events.
8. **Grants and Funding**: Seek funding from government grants, agricultural research organizations, or venture capital firms interested in supporting innovations in agriculture and sustainable water management. Use this funding to further develop and promote the tool.
By combining one or more of these monetization strategies, you can create a sustainable business model around a Crop Irrigation Scheduling Tool that provides value to farmers while generating revenue for your enterprise.
More you want to know please visit, https://sahidulsir.blogspot.com.