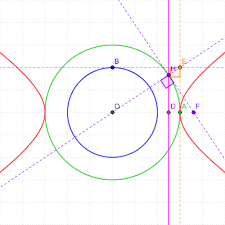
Defination: A hyperbola is a type of conic section, along with circles, ellipses, and parabolas. It's defined as the set of all points in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference of the distances from two fixed points (called the foci) is constant. In other words, for a hyperbola, the difference in distances from any point on the curve to the two foci remains constant.
Click the Translate button(see right) on this post to set your Own Language to understand more perfectly!!
Hyperbola Calculator
Continue Definition:
A hyperbola is a type of conic section, along with circles, ellipses, and parabolas. It's defined as the set of all points in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference of the distances from two fixed points (called the foci) is constant. In other words, for a hyperbola, the difference in distances from any point on the curve to the two foci remains constant.
Equation of a Hyperbola:
The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola centered at the origin with its transverse axis along the x-axis is:
{
The standard form of the equation of a hyperbola centered at the origin with its transverse axis along the y-axis is:y^2}/{a^2} - {x^2}/{b^2} = 1
where:
(a) is the distance from the center to either vertex along the x-axis (semi-major axis),
(b) is the distance from the center to either endpoint of the conjugate axis along the y-axis (semi-minor axis).
The foci of the hyperbola are located along the x-axis at the points
( c, 0)), where (c = sqrt{a^2 + b^2+b}).
Properties of a Hyperbola:
1. **Center**: The center of the hyperbola is the point ((0, 0)\) if the hyperbola is centered at the origin.
2. **Vertices**: The vertices of the hyperbola are the points where it intersects its transverse axis.
3. **Foci**: The foci are the two fixed points inside the hyperbola.
4. **Asymptotes**: Hyperbolas have asymptotes, which are lines that the curve approaches but never intersects.
5. **Transverse Axis**: The axis passing through the vertices is called the transverse axis.
6. **Conjugate Axis**: The axis perpendicular to the transverse axis, passing through the center, is called the conjugate axis.
7. **Eccentricity**: The eccentricity of a hyperbola is the ratio of the distance from any point on the hyperbola to one of the foci over the distance from the same point to the corresponding directrix. It is denoted by (e) and is always greater than 1 for hyperbolas.
Examples of Hyperbolas:
1. **Satellite Orbits**: The paths of satellites around the Earth often follow hyperbolic trajectories.
2. **Conic Sections**: Hyperbolas can be found in nature as conic sections formed by intersecting a plane with a double cone.
3. **Optics**: Hyperbolic mirrors are used in certain types of telescopes and antennas to focus or reflect electromagnetic waves.
4. **Engineering**: Hyperbolic shapes are used in architecture and engineering, such as in the design of cooling towers or suspension bridges.
5. **Mathematics**: Hyperbolas are studied extensively in mathematics for their geometric properties and applications in various fields, including calculus and geometry.
How it is possible to EARN MONEY using Hyperbola Calculation in real life?????
Earning money directly through hyperbola calculations may be less common compared to other applications of mathematics. However, a strong understanding of hyperbolas and their properties can lead to opportunities in various fields where mathematical skills are valued. Here are some ways individuals can leverage hyperbola calculations to potentially earn money in real life:
1. **Engineering and Design Services**: Offer engineering or design services where hyperbolas are relevant, such as in the design of satellite trajectories, antennas, or architectural structures. A deep understanding of hyperbolas and their properties can be valuable in optimizing designs for efficiency and performance.
2. **Aerospace Industry**: Work in the aerospace industry, where hyperbolic trajectories are used in spacecraft navigation, orbit determination, and mission planning. Individuals with expertise in hyperbola calculations can contribute to the development and execution of space missions.
3. **Optics and Imaging Technologies**: Hyperbolas are used in optics for designing certain types of mirrors and lenses. Specialized knowledge of hyperbolas can be beneficial in industries involving optical systems, such as photography, astronomy, or laser technology.
4. **Math Tutoring and Education**: Offer tutoring services in mathematics, including geometry and conic sections. Hyperbolas are a fundamental topic in mathematics education, and individuals with expertise in this area can provide valuable instruction to students at various levels.
5. **Software Development**: Develop software tools or applications that utilize hyperbola calculations for specific purposes, such as simulation software for engineering or scientific research. These tools can be sold or licensed to companies and professionals in relevant industries.
6. **Consulting Services**: Provide consulting services to companies or research institutions that require expertise in hyperbola calculations for specific projects or applications. Consulting opportunities may arise in fields such as physics, geodesy, or telecommunications.
7. **Data Analysis and Modeling**: Use hyperbola equations and properties in mathematical modeling and data analysis for various applications, such as predicting trends, optimizing processes, or solving complex problems. Individuals with skills in mathematical modeling can find employment in industries like finance, economics, or environmental science.
8. **Research and Development**: Work in research and development roles where hyperbola calculations are essential for innovation and problem-solving. Industries such as defense, aerospace, and telecommunications often require research scientists and engineers with expertise in advanced mathematics.
While direct opportunities to earn money solely through hyperbola calculations may be limited, individuals with a strong mathematical background and expertise in hyperbolas can apply their skills in diverse fields where mathematical reasoning and problem-solving are valued.
Do YOU Want To Earn Money In Various Ways, Click The Link & Explore Your Field of Interest!!!